Fungus flown for weed fight
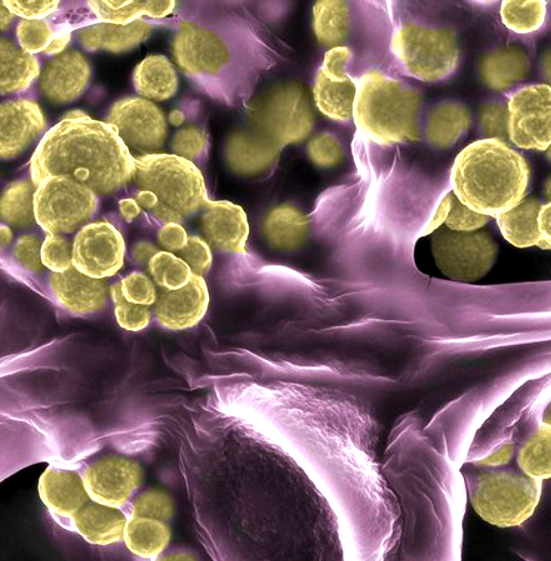 CSIRO says a new fungus can help farmers fight a fast-spreading weed.
CSIRO says a new fungus can help farmers fight a fast-spreading weed.
Flaxleaf fleabane causes grain crop revenue losses of more than $43 million each year.
CSIRO scientists are piloting the release of a fungus from Columbia to help farmers tackle the weed.
CSIRO weed ecologist, Dr Ben Gooden, says flaxleaf fleabane is one of the most difficult-to-control weeds in grain cropping systems, and is estimated to affect nearly three million hectares of land in Australia.
“As flaxleaf fleabane has developed resistance to some herbicides, we hope that the biocontrol agent will be effective in reducing its populations across the country,” Dr Gooden says.
“We identified a rust fungus called Puccinia cnici-oleracei in Colombia which infects flaxleaf fleabane and restricts it from growing by destroying the plant’s tissues,” he said.
The fungus was imported into CSIRO’s high-security quarantine facility in Canberra where scientists studied it extensively to determine if it would be safe to introduce to Australia as a biocontrol agent.
“Our research found the fungus can only infect flaxleaf fleabane, while all non-target plant species tested were resistant to it. Based on this research, the fungus is deemed to be safe and has been approved by the Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry for introduction to Australia,” Dr Gooden said.
Flaxleaf fleabane grows up to one metre and is a prolific seed producer. Each plant can produce over 100,000 seeds and these can disperse long distances with the help of wind, water, animals, and vehicles, explaining its rapid spread not just within local districts but into southern and western cropping and grazing regions in recent times.
The Grains and Research Development Corporation (GRDC) was one of the supporting organisations for the research.
GRDC’s Dr Jason Emms says grain growers have been battling flaxleaf fleabane for many years as the weed competes for soil water across multiple stages of the crop cycle, which directly impacts production.
“Flaxleaf fleabane can run rampant during the fallow phase as there is little competition for light or moisture. Once established it is very difficult to control,” Dr Emms says.
“A biocontrol agent for this problematic weed is very exciting as it may help to reduce overall populations when integrated with existing weed management strategies,” he said.








 Print
Print